Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment – Advanced Facial Injury Care & Emergency Oral Surgery Solutions by DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic in Bargarh, Odisha
Maxillofacial trauma is a true medical emergency. Injuries to the face and jaw can compromise breathing, cause severe hemorrhage, damage critical sensory functions (vision, smell, taste), disrupt eating and swallowing, and create devastating aesthetic consequences affecting a patient’s appearance and psychological well-being. The complexity lies in the fact that facial injuries involve not just bone but delicate soft tissues, critical nerves, blood vessels, and structures essential to basic human functions. At Dr. Khuntia’s Dental Clinic, we are equipped with the expertise and technology to handle such emergencies, providing prompt, precise care to restore both function and aesthetics.
Every year, thousands of individuals suffer maxillofacial trauma through road accidents, sports injuries, falls, and interpersonal violence. The International Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons reports that approximately 17% of all primary facial fractures are associated with road traffic accidents alone, with mandibular fractures (jaw) being the most common, followed by orbital, nasal, and frontal fractures. Sports-related facial injuries are equally significant, with research showing that facial injuries comprise roughly 20% of all sports injuries among high school athletes, with baseball, lacrosse, and basketball being the highest-risk sports.
The critical difference between standard dental care and maxillofacial trauma management lies in the urgency and complexity of treatment. While routine dental procedures, such as those offered in orthodontic treatments, can often be scheduled for a later time, facial trauma requires immediate assessment and frequently emergency surgical intervention. For example, orthodontic treatments focus on correcting dental misalignments and improving long-term oral health, but in the case of trauma, minutes can mean the difference between saving a tooth or losing it permanently. In addition, laser dentistry can help with certain injuries by promoting faster healing and reducing infection risks, but hours can determine whether facial function is preserved or compromised.
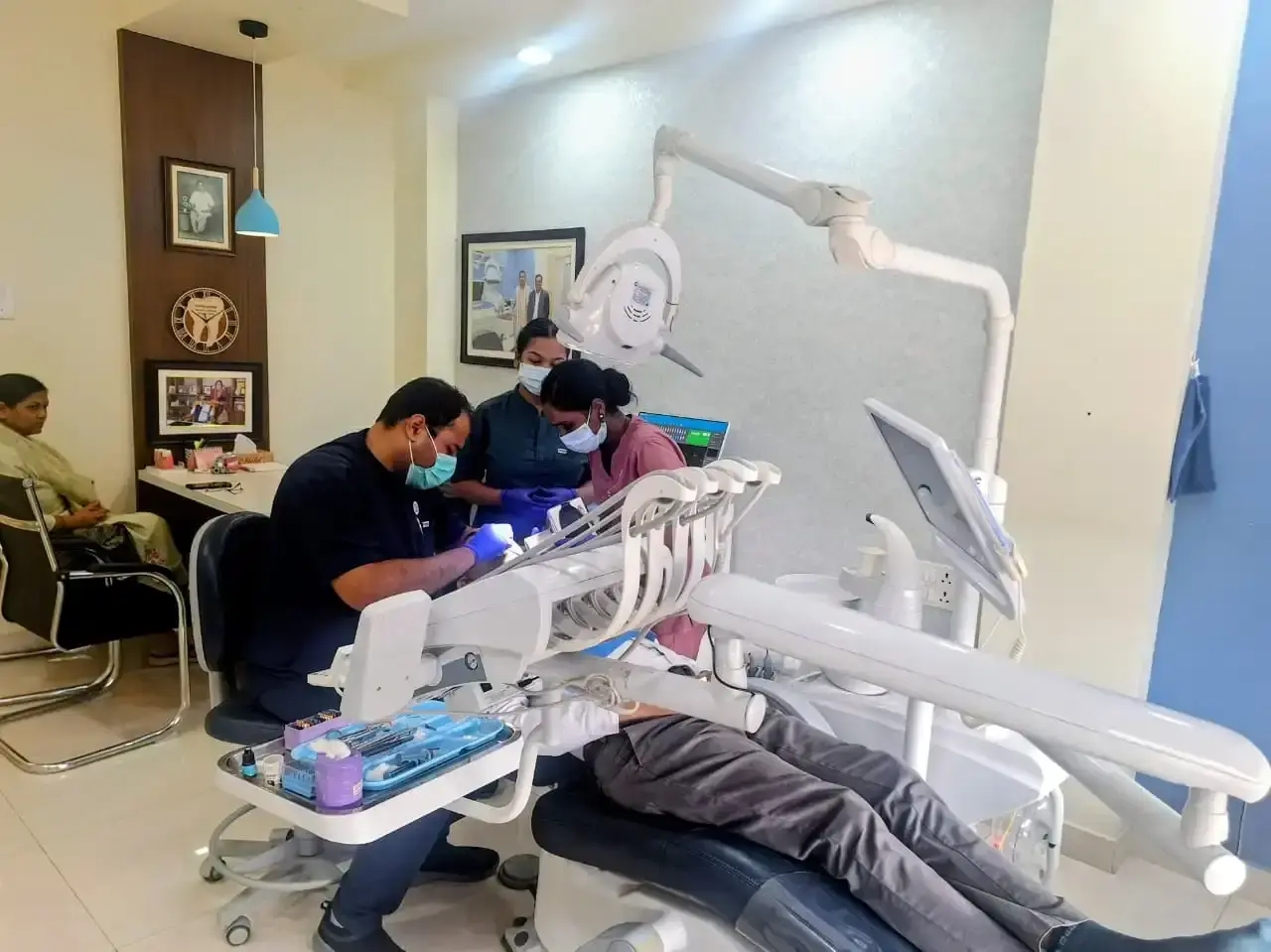
At DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic in Bargarh, Odisha, we recognize the life-altering consequences of facial trauma. Our specialized oral and maxillofacial surgery team is equipped, trained, and available to provide emergency care for facial injuries of any severity. We combine advanced diagnostic technology with surgical expertise refined through years of managing complex trauma cases. Our goal is simple but profound: restore your facial function, minimize aesthetic complications, and support your complete recovery back to normal life.
Maxillofacial Trauma: Complete Overview & Fundamental Concepts
Maxillofacial trauma encompasses injuries to the facial skeleton, soft tissues, teeth, and associated structures. Unlike isolated dental injuries that might be managed in a routine dental office, maxillofacial trauma often requires emergency oral and maxillofacial surgery—a specialized surgical field requiring additional training beyond general dentistry. While general dentistry addresses common dental issues like cavities and preventive care, maxillofacial trauma involves more complex situations that may necessitate immediate surgical intervention to preserve both function and aesthetics. Additionally, in pediatric cases, preventive dentistry plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of future trauma by ensuring the early development of strong, healthy teeth.
Common Types of Maxillofacial Injuries
Skeletal/Bone Injuries: - Mandibular (Lower Jaw) Fractures: The most common facial fracture, particularly vulnerable due to its prominent position; ranges from simple fractures to complex multi-segment breaks - Maxillary (Upper Jaw) Fractures: Range from Le Fort I, II, or III fractures (specific patterns of upper facial fracture defined by surgical classification) to simple alveolar bone breaks - Zygomatic (Cheekbone) Fractures: Common in assault and sports injuries; affects cheek prominence and eye socket position - Nasal Bone Fractures: Most common facial fracture overall but often managed simply; important to address immediately to prevent permanent deformity - Orbital (Eye Socket) Fractures: Potentially serious if associated with eye injury; requires careful assessment - Frontal Bone Fractures: Relatively uncommon but potentially serious if involving skull base
Dental Injuries: - Tooth Fractures: Ranging from simple crown fractures to root fractures requiring extraction - Tooth Luxation/Subluxation: Tooth displacement from socket; often can be repositioned and splinted if treated immediately - Tooth Avulsion: Complete tooth separation from socket; salvageable if replanted within 30-60 minutes - Alveolar Bone Fractures: Fracture of bone surrounding tooth roots; affects tooth stability
Soft Tissue Injuries: - Facial Lacerations: Cuts of varying depth requiring meticulous closure to minimize scarring - Lip Injuries: Particularly important given visibility and functional importance; require specialized closure techniques - Intraoral Soft Tissue Damage: Injuries inside mouth affecting gums, cheeks, palate, tongue
Other Injuries: - TMJ (Temporomandibular Joint) Trauma: Jaw joint injuries affecting bite and jaw function - Nerve Injuries: Facial nerve or trigeminal nerve damage causing sensory loss or paralysis - Vascular Injuries: Damage to blood vessels requiring hemostasis and possible vascular repair
Causes of Maxillofacial Trauma
Road traffic accidents are a leading cause of facial fractures, accounting for about 17% of all primary facial injuries. These accidents often result in multiple injuries, and because they may involve other body trauma, they require careful coordination with a trauma team. The severity of these injuries is typically predictable due to the high-impact forces involved. In such cases, specialized care for facial trauma is critical, as it can significantly affect both functionality and appearance. Comprehensive facial trauma treatment focuses on stabilizing the facial structure and minimizing long-term complications. After the trauma is managed, patients may turn to cosmetic dentistry to restore the aesthetic appearance of their smile, helping them recover both physically and emotionally from the traumatic experience.
Sports Injuries - Highest in baseball, lacrosse, basketball (contact/collision sports) - Nasal fractures most common, followed by midface and mandibular fractures - Professional athletes experience higher injury rates than amateurs - Combat sports (kickboxing, MMA) have 69-79% facial injury rates among participants
Interpersonal Violence/Assault - Significant cause of maxillofacial trauma worldwide - Often associated with psychological trauma requiring multidisciplinary care
Falls - Particularly in pediatric and elderly populations - Often preventable with safety measures - May indicate underlying balance or neurological issues requiring investigation
Workplace/Industrial Accidents - Varying severity depending on mechanism and equipment involved
Why Immediate Expert Care Matters
The window for optimal outcomes in maxillofacial trauma is extremely narrow: - Tooth Avulsion: 30-60 minutes for best replantation success rates - Bone Fracture Reduction: Within hours to achieve optimal alignment - Soft Tissue Repair: Within 24 hours for best cosmetic outcomes and infection prevention
Delayed or inadequate treatment of facial trauma can lead to serious and long-lasting consequences, including permanent tooth loss, chronic pain, and TMJ dysfunction. It can also result in persistent malocclusion (improper bite), permanent sensory loss (such as numbness or tingling), aesthetic deformities, and functional impairments, making it difficult to eat, speak, or breathe. Additionally, untreated injuries can lead to infections and more complex secondary surgeries. To avoid these complications, immediate and effective care is essential. For urgent situations, emergency dental care provides rapid intervention to address acute issues and prevent further damage. In cases of tooth loss, dental implants can offer a long-term solution, helping to restore both the function and aesthetics of a patient's smile.
At DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic, we understand these critical timelines and provide immediate expert assessment and treatment.
Key Features & Advantages of Advanced Maxillofacial Trauma Care
Advanced Maxillofacial Trauma Care & Facial Injury Management Excellence
Comprehensive Trauma Assessment
Our emergency protocol ensures nothing is missed:
Primary Survey (ABCDE Approach) - Airway: Assess airway patency; secure airway if compromised due to swelling, blood, or structural damage - Breathing: Ensure adequate oxygen exchange - Circulation: Control bleeding; assess for shock - Disability: Neurological assessment - Exposure: Thorough examination of all injuries
Secondary Survey - Detailed facial examination assessing all injuries - Dental and intraoral injury assessment - Occlusion (bite) evaluation - Sensory testing for nerve injuries - Comprehensive documentation for surgical planning
Clinical Excellence: Our team’s trauma expertise ensures systematic, thorough assessment that prevents injuries from being missed while prioritizing life-threatening conditions.
Emergency Jaw Fracture Treatment & Oral Surgery Solutions
Immediate Jaw Fracture Management
Mandibular and maxillary fractures require specialized treatment:
Immediate Stabilization - Pain control (local anesthesia, systemic analgesics) - Hemostasis (controlling bleeding) - Temporary stabilization preventing further displacement - Positioning to maintain airway patency
Diagnostic Imaging - Multiple X-ray views (PA, lateral, occlusal) showing fracture lines and displacement - Panoramic radiograph for overall jaw assessment - CT imaging for complex cases showing three-dimensional fracture pattern - Virtual surgical planning for optimal reduction strategy
Treatment Planning - Assessment of fracture type (simple, comminuted, displacement degree) - Determination of surgical vs. conservative management - Optimization of treatment to restore proper occlusion and jaw alignment
Surgical Intervention For displaced or complex fractures requiring surgical fixation: - Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF): Small plates and screws securing fracture fragments in anatomic position - Surgical approach carefully selected (intraoral minimizing external scarring when possible) - Intraoperative verification ensuring proper alignment and bite - Soft tissue closure minimizing complications and infection risk
Functional Restoration Success metrics include: - Proper occlusion (correct bite relationship) - Mouth opening restoration (typically >35mm) - Pain-free function - Absence of TMJ clicking or dysfunction - Absence of infection
Clinical Success: Studies show that 59% of maxillofacial trauma patients require surgical intervention. Our advanced surgical techniques achieve healing and functional restoration in 50% of patients within 20 days of injury, with average recovery times of 21 days for jaw injuries.
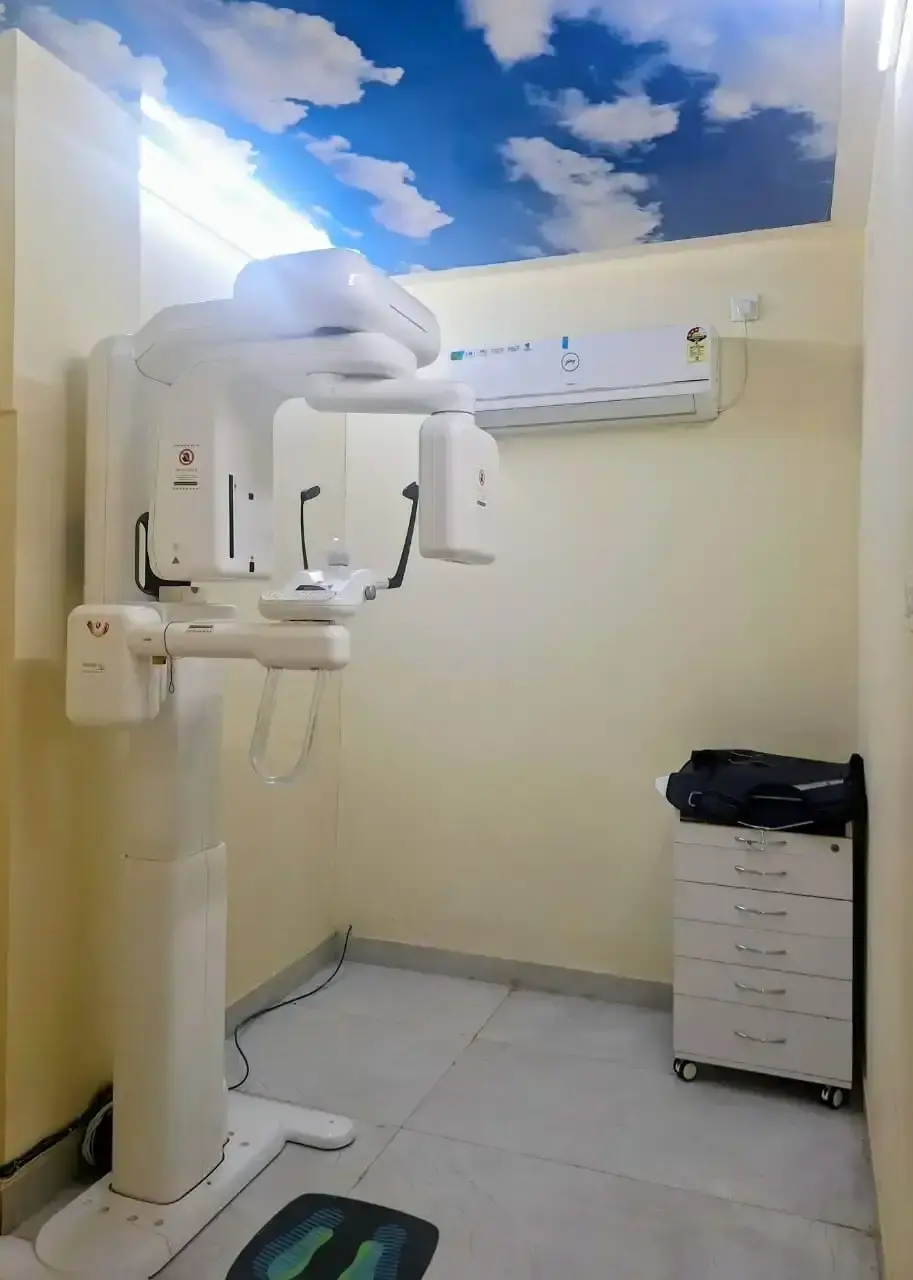
Precision Diagnosis with CT, X-rays & Digital Imaging
Advanced Diagnostic Technology
Accurate diagnosis is a prerequisite to optimal treatment. Our advanced imaging capabilities, available through our state-of-the-art healthcare services, ensure precise and effective results. For more information about the cutting-edge technology and comprehensive care we provide, visit our hospital services page:
Digital Radiography - Low-radiation digital X-rays providing detailed skeletal imaging - Multiple views enabling complete assessment of fracture extent - Instant image review and enhancement - Superior clarity to traditional film
Panoramic Radiography - Full-jaw overview in single image - Excellent for fracture screening - Shows bilateral comparison - Identifies multiple fractures
CT Imaging (Computed Tomography) - Complete 3D anatomical reconstruction - Shows fracture patterns in three dimensions - Enables virtual surgical planning - Critical for complex multi-segment fractures - Shows soft tissue and vascular involvement - Identifies associated injuries (brain, spine, other organs)
Intraoral Imaging - High-resolution photography showing intraoral injuries - Dental damage assessment - Alveolar bone fracture visualization - Soft tissue injury documentation
Virtual Surgical Planning - 3D reconstruction enabling precise pre-operative planning - Computer-assisted determination of optimal reduction - Prediction of final occlusion - Reduction of operative time - Improved surgical outcomes
Clinical Advantage: Advanced imaging allows us to understand injury complexity fully, plan optimal treatment, and communicate clearly with patients about their injuries and expected outcomes.
Patient Safety, Pain Control & Faster Healing Protocols
Comprehensive Safety Standards
Infection Prevention - Prophylactic antibiotics per evidence-based guidelines (within 3 hours of injury for open fractures) - Meticulous wound debridement removing devitalized tissue - Aseptic surgical technique with standard sterilization protocols - Antimicrobial irrigation during surgery - Post-operative antibiotic coverage when indicated - Regular post-operative monitoring for infection signs
Pain Management - Local anesthesia for wound exploration and closure - Systemic analgesia (acetaminophen, NSAIDs, opioids if needed) for post-operative pain - Regional blocks for specific injuries - Non-pharmacological comfort measures (ice, positioning, support) - Clear discharge instructions for pain management at home
Swelling Control - Ice application in acute phase - Elevation reducing gravitational fluid accumulation - Anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) - Compression dressings for soft tissue injuries - Lifestyle modifications (head elevation during sleep)
Surgical Hemostasis - Meticulous intraoperative hemostasis preventing post-operative bleeding complications - Careful vessel identification and preservation - Appropriate use of hemostatic agents if needed - Drain placement in extensive injuries - Post-operative bleeding monitoring
Nutritional Support During Healing - Soft or liquid diet during jaw healing when necessary - Adequate protein and micronutrients supporting bone healing - Hydration support - Nutritionist consultation for optimized post-operative nutrition
Faster Healing Protocols - Optimal surgical technique minimizing tissue trauma - Proper immobilization/fixation preventing micromotion that delays healing - Early mobilization (gentle mouth opening exercises) preventing stiffness - Proper oral hygiene during healing - Tobacco and alcohol avoidance (both delay healing) - Stress management supporting immune function
Research-Based Results: With evidence-based care, functional recovery times average 20 days for zygomatic injuries and 21 days for mandibular injuries. Proper early intervention dramatically improves long-term outcomes.
Comprehensive Facial Reconstruction & Rehabilitation
Beyond Immediate Stabilization to Complete Restoration
Soft tissue reconstruction for significant tissue loss or complex injuries encompasses various techniques tailored to the severity of the defect. For small-to-moderate defects, local flaps using adjacent tissue are typically used, while larger defects may require regional flaps. In cases of massive defects, free tissue transfer—a complex procedure requiring microsurgical expertise—is performed. Additionally, scar revision can enhance aesthetic outcomes months or even years after the injury. For alternative treatments, you can explore Homeopathy services or visit our clinics for specialized care.
Bone Reconstruction - Bone grafting for gaps created by fracture or tissue loss - Autogenous bone (patient’s own bone) providing optimal integration - Synthetic bone substitutes reducing need for second surgery - Vascularized bone flaps for critical weight-bearing areas
Dental Rehabilitation - Tooth replantation for avulsed teeth treated immediately - Orthodontic movement of teeth restored to proper position - Prosthetic replacement (bridges, implants) for teeth unable to be saved - Comprehensive bite rehabilitation
Functional Restoration - Restoration of chewing function - Restoration of speech clarity - Restoration of swallowing - TMJ function restoration
Aesthetic Optimization - Scar revision and camouflage - Symmetry restoration - Contouring corrections - Revision surgery if needed to optimize appearance
Psychological Support - Recognition that facial trauma carries significant psychological impact - Referral to mental health professionals when needed - Patient education about expected recovery timeline - Support groups for trauma patients
Detailed Service Categories: Complete Maxillofacial Trauma Solutions
Facial Soft Tissue Injury Repair – Minimizing Scarring While Restoring Function
Understanding Soft Tissue Injuries
Facial soft tissues include skin, mucous membrane, muscle, and deeper structures. Different injuries require different techniques to ensure proper healing. For dental-related issues, our dental clinics offer specialized care. Additionally, for holistic treatment approaches, explore our Ayurveda services to support recovery and overall well-being:
Abrasions & Minor Lacerations (<1cm) - Wound cleaning and removal of debris - Simple closure with sutures - Healing: 5-7 days
Moderate Lacerations (1-5cm) - Proper layered closure (muscle, then mucosa/submucosa, then skin) - Use of absorbable sutures for deep layers - Meticulous skin closure for cosmetic outcome - Healing: 7-14 days for suture removal; complete healing 2-3 weeks
Complex Lacerations (>5cm, involving structures like lips or eyelids) - Highly specialized technique required - Lip Injuries: Critical closure technique preserving vermilion border (junction between lip and skin); muscle layer separately closed for cosmetics; skin edges precisely aligned - Eyelid Injuries: Margin-to-margin precise alignment preventing entropion/ectropion; requires specialized technique - Deep Structure Involvement: Assessment and repair of muscle, nerves, or blood vessels - Healing: Variable; often requires secondary procedures for optimization
Avulsive Injuries (Tissue Completely Removed) - Debriding remaining tissue - Primary closure of defect if possible (wedge resection and linear closure for lips) - Tissue grafting if gap too large to close primarily - Local or distant flaps for reconstruction - Healing: 3-6 weeks for simple closures; months for complex reconstructions
Intraoral Soft Tissue Injuries - Gingival Lacerations: Suturing of gum tissue; preservation of tooth-supporting structures - Palatal Injuries: Layered closure restoring barrier function - Cheek or Tongue Lacerations: Restoration of mucosa; preservation of function - Healing: 1-2 weeks (oral mucosa heals quickly due to excellent blood supply)
Infection Prevention in Soft Tissue Injuries - Prophylactic antibiotics (especially for “dirty” or puncture wounds) - Proper wound cleaning and removal of foreign material - Regular post-operative wound assessment - Clear signs of infection to watch for (increasing redness, swelling, warmth, drainage)
Scar Management - Immediate: Proper wound closure technique minimizing scar visibility - Early (weeks 1-4): Scar care with silicone gels or sheets - Ongoing (months): Scar maturation; massage may improve appearance - Late (6-12 months): Laser resurfacing or scar revision if needed
Jaw Fracture (Mandible & Maxilla) Management – Restoring Bite & Function
Mandibular Fracture Treatment
Mandibular fractures (jaw) are the most common facial fractures, and treatment depends on the type and complexity of the fracture. For comprehensive care and recovery, our nursing homes provide specialized services. Additionally, for patients requiring psychological support during their recovery, our mental health hospital offers dedicated care to ensure overall well-being.
Simple Fractures (Non-displaced, minimal soft tissue damage) - Conservative management possible - Soft diet (4-6 weeks) - Pain management - Regular monitoring for proper healing - Success: 80-90% heal without surgery
Displaced Fractures (Fragments misaligned) - Often require surgical fixation - Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF) - Small titanium or stainless steel plates and screws - Secure fracture fragments in anatomically correct position - Allows earlier return to function (can eat softer foods sooner) - Faster healing: 3-6 months vs. 4-6 weeks conservative management
Complex Fractures (Multiple segments, severe displacement) - Multiple plates often needed - May require specialized surgical approaches - Virtual surgical planning optimizing approach - Extended recovery and careful post-operative monitoring
Special Considerations - Condylar Fractures (jaw joint): Conservative management often preferred in children (prevents surgery interfering with growth); surgical management in adults if significantly displaced - Parasymphyseal Fractures: Common site; requires careful fixation preserving anterior tooth segment - Edentulous Patients (no teeth): Requires different fixation strategy since standard arch bars can’t be used
Post-Operative Protocol - Soft diet for initial healing period - Gentle mouth-opening exercises preventing stiffness - Regular follow-up monitoring bite and function - Imaging verification of proper healing - Hardware removal once bone healing complete (typically 6-12 months)
Success Metrics - Proper occlusion restored - Mouth opening >35mm - Pain-free function - No infection - No TMJ dysfunction
Maxillary Fracture Treatment
Maxillary (upper jaw) fractures are less common than mandibular but equally important.
Le Fort Fractures The classification system describes specific patterns: - Le Fort I: Horizontal fracture separating upper teeth and palate from rest of face - Le Fort II: Pyramid-shaped fracture involving upper teeth, palate, and nasal bones - Le Fort III: Severe fracture separating upper face and palate from middle face (surgical emergency)
Treatment - ORIF with plates and screws - Restoration of facial projection (maxillary fractures commonly cause facial collapse) - Detailed attention to occlusion - Often requires interdisciplinary approach (orthodontics for bite correction)
Recovery - Surgical healing: 3-6 months for bone - Return to function: Variable based on severity - Extended nutrition support often needed
Dental Trauma & Avulsed Tooth Management – Time-Critical Treatment
Traumatic Dental Injuries
Teeth are frequently injured in maxillofacial trauma, and immediate expert treatment dramatically improves outcomes. For access to necessary medications, our pharmacy provides a wide range of treatments. Additionally, for pharmaceutical needs, you can explore our pharmaceuticals and chemical products to support recovery and healing.
Tooth Fracture - Uncomplicated Crown Fractures (doesn’t involve pulp/nerve): Composite restoration restoring anatomy - Complicated Crown Fractures (exposes pulp): Pulp cap or endodontic treatment required; restoration afterward - Root Fractures: Variable prognosis depending on fracture location and degree of displacement; splinting and monitoring often required
Tooth Luxation (Tooth Displaced But Still in Socket) - Subluxation (slight displacement): Splinting 2+ weeks; monitor for pulp damage - Intrusion (tooth pushed into socket): Repositioning and stabilization; careful monitoring; may require orthodontic traction - Extrusion (tooth partially out): Repositioning into socket and splinting
Tooth Avulsion (Tooth Completely Out of Socket) - TRUE EMERGENCY
This is the most time-sensitive dental injury. Prognosis directly correlates with time outside socket.
What To Do Immediately (Within Minutes):
1. Find the Tooth: Locate and handle carefully—avoid touching root surface
2. If Possible, Reinsert Immediately: Place tooth back in socket if conscious patient can cooperate
3. If Can’t Reinsert: Keep tooth moist - Best option: Store in milk (preserves periodontal ligament cells) - Alternative: Store in patient’s mouth (saliva provides moisture) - Never: Store in water or dry
4. Seek Emergency Care Immediately: Time is critical
Prognosis Based on Time Out of Socket: - 0-30 minutes: 85-90% success rate for replantation - 30-60 minutes: 50-70% success rate - 1-2 hours: 5-10% success rate - >2 hours: Very low success; extraction often necessary
Treatment at Clinic: 1. Assessment: Visual inspection; radiographs showing root condition 2. Pulp Status: Evaluation of tooth’s ability to survive 3. Replantation: Careful placement back into socket in correct position 4. Splinting: Stabilization for 2 weeks allowing periodontal ligament healing 5. Bite Adjustment: Ensuring no premature contact 6. Follow-up: Regular monitoring for infection; endodontic treatment typically needed within 2-4 weeks 7. Long-term Monitoring: Assessment of tooth vitality over months
Success Factors: - Time out of socket (critical) - Storage medium (milk best) - Root development status (mature roots slightly better prognosis) - Splinting technique - Patient compliance with soft diet and oral hygiene
Alveolar Bone Fractures (Fracture of bone around tooth roots) - Often occurs with avulsed teeth or significant dental displacement - Can affect tooth stability and prognosis - Requires careful assessment and sometimes surgical management
Road Accident Facial Injury Care – Comprehensive Multi-Injury Management
The Challenge of Road Trauma
Road traffic accidents (RTAs) represent the largest single cause of maxillofacial trauma. These injuries are distinctive in several ways, requiring specialized care from experienced professionals. Our doctors are equipped to handle such complex cases, and for comprehensive support, our health professionals provide coordinated care throughout the recovery process.
Characteristics of RTA Injuries - High Force Impact: Impacts from vehicles, dashboards, steering wheels cause severe injuries - Multiple Injuries: Often facial trauma combined with other body injuries (head, neck, chest, extremities) - Complexity: Often involve multiple facial structures simultaneously - Associated Injuries: Brain injury, cervical spine injury, other trauma requiring coordinated care
Epidemiology - 17% of all primary facial fractures - Mandibular fractures most common (23%) - Frontal fractures (14%) - Orbital fractures (14%) - Approximately 50% more likely to have multiple facial fractures than other trauma mechanisms
Emergency Management Protocol
Primary Survey (ABCDE) - Airway Protection: Maxillofacial trauma can compromise airway through blood, swelling, or bone displacement; requires careful airway management - Breathing Assessment: Ensure adequate oxygenation - Circulation Control: Control hemorrhage; manage shock if present - Disability Assessment: Neurological examination; assess for head/spine injury - Exposure: Complete examination identifying all injuries
Hemorrhage Control - Direct pressure on facial bleeding - Careful intraoral packing if needed (avoiding airway compromise) - Posterior nasal packing if epistaxis present - Identification and possible ligation of major vessels if needed
Airway Management - Clearing airway of blood, debris, broken teeth - Positioning preventing aspiration - Intubation if airway compromise (nasal if possible; oral if base of skull fracture present) - Surgical airway (cricothyrotomy) if needed for complete obstruction
Stabilization & Transfer - Careful cervical spine stabilization (assume spine injury until proven otherwise) - Transport to facility equipped for comprehensive trauma care - Coordination with trauma team managing other injuries
Comprehensive Facial Assessment - Once stable, detailed facial examination identifying all injuries - Imaging (CT scan typically) assessing extent of injury - Treatment planning addressing multiple injuries in priority order
Surgical Management - Coordination with other surgical specialties if multiple injuries - Fracture fixation via ORIF - Soft tissue repair - Dental rehabilitation - Often staged procedures addressing injuries in priority order
Timeline Challenges - Swelling develops rapidly after trauma, making surgery increasingly difficult - Early intervention (ideally within 24-48 hours) optimizes outcomes - However, other life-threatening injuries may take priority
Recovery and Rehabilitation - Extended recovery from multiple injuries - Multidisciplinary care (trauma surgery, oral surgery, physical therapy, psychology) - Potential long-term disability requiring support services
Sports Injury Maxillofacial Treatment – Getting Athletes Back in Action Safely
The Growing Challenge of Sports Trauma
Sports-related facial injuries are becoming increasingly common. Research shows that facial injuries comprise about 20% of all sports injuries in high school athletes, with baseball, lacrosse, and basketball having the highest incidence rates. Combat sports such as kickboxing and MMA have facial injury rates ranging from 69-79%. The most common injuries include nasal fractures, dental trauma, and midface fractures. For mental health support in managing the impact of these injuries, our psychiatrists can offer specialized care. Additionally, our medical assistants are available to provide essential support during recovery.
Sports-Specific Injury Patterns
Baseball - Midface fractures most common (from ball impact) - Dental injuries common - Annual incidence rate for midface fractures: 0.017% in high school athletes - Often treated acutely allowing return to season
Lacrosse - Mandibular (jaw) fractures most common (from stick impact) - High-contact sport with significant injury risk - Annual incidence rate for mandible fractures: 0.037% - Often requires surgery with 4-6 week recovery
Basketball - Nasal fractures most common - Variety of injury mechanisms (contact, falls) - Generally less severe than lacrosse/baseball - Often heal with conservative management
Combat Sports - 69% of kickboxers have facial injuries - Professional athletes have higher injury rates (86%) than amateurs (42%) - Nasal injuries most common; dental and jaw injuries also frequent
Treatment Considerations
Acute Management - Immediate assessment determining severity - Control of bleeding and swelling - Pain management - Determination of need for imaging - Assessment of return-to-play safety
Definitive Treatment - Stabilization of fractures (surgical or conservative depending on type) - Dental rehabilitation if teeth affected - Clearance ensuring safe return to sport
Return-to-Play Protocols - Clearance only after adequate healing - Face protection requirements (specific to sport and injury type) - Progressive return to full activity - Monitoring for complications
Timeline for Return - Simple nasal fractures: Often 2-3 weeks with protective equipment - Dental injuries: Depends on tooth viability and treatment - Mandibular fractures: 4-8 weeks depending on treatment and healing - Midface/orbital fractures: 6-12 weeks or more
Prevention Focus - Evidence strongly supports face protection in sports with high injury rates - Mouthguards particularly effective preventing dental injuries - Protective eyewear in ball sports - Proper tackling/contact technique training
Emergency Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery – Surgical Expertise Under Pressure
Defining Emergency Oral Surgery
Emergency oral and maxillofacial surgery addresses life-threatening or function-threatening conditions requiring surgical intervention under time pressure. During such critical situations, the support of skilled nurses is vital to ensure patient stability and care. For recovery and holistic healing, our beauty and wellness services offer additional treatments to support overall well-being after surgery.
Emergency Indications - Airway compromise from facial trauma - Uncontrolled hemorrhage - Mandibular fractures with severe displacement requiring immediate reduction - Tooth avulsion requiring immediate replantation - Soft tissue injury requiring immediate repair - Nerve compression - Compartment syndrome
Surgical Principles
Assessment - Rapid but thorough evaluation - Imaging when available without compromising time-critical treatment - Identification of life-threatening conditions requiring immediate intervention - Planning surgical approach balancing speed with optimal technique
Surgical Technique - Efficient but not rushed - Use of surgical approaches minimizing additional trauma - Meticulous hemostasis preventing post-operative bleeding complications - Attention to cosmetics even in emergency setting - Intraoperative verification of correction
Anesthesia - Safe but efficient anesthesia management - Careful airway management in trauma patients - Adequate pain control without overdosing - Monitoring for complications
Post-Operative Management - Intensive early monitoring - Pain control - Swelling management - Infection prevention - Clear discharge instructions
Clinical Expertise: Our surgeons have experience managing complex emergency situations, providing calm, expert care under pressure when time is critical.
Bone Fixation & Trauma Stabilization Techniques
Understanding Bone Fracture Fixation
The goal of fixation is to hold fractured bone fragments in an anatomically correct position while the bone heals. Once healing is complete, additional treatments, such as those offered through our beauty and wellness hair transplant services, can support recovery and restore confidence. For any home-based care needs during recovery, our home services ensure convenient and effective support right at your doorstep.
Fixation Methods
Conservative Management (No Surgery) - Appropriate for non-displaced or minimally displaced simple fractures - Soft diet maintaining facial position - Medications for pain and swelling - Close monitoring ensuring proper healing - Success: 80-90% heal without complications
Wire Fixation (Maxillomandibular Fixation) - Wires attached to teeth holding jaws in proper relationship - Used increasingly less as surgical plates more effective - Still useful in specific situations - Requires adequate dentition - Recovery: 4-6 weeks
Plate and Screw Fixation (ORIF - Open Reduction Internal Fixation) - Most common modern technique - Small titanium or stainless steel plates with screws - Allows immediate return to function (soft diet possible immediately) - Faster healing: 3-6 months - Requires surgical incision for placement - Slightly higher cost than conservative management - Superior outcomes particularly for displaced fractures
Implant Cages/Reconstruction Plates - For complex fractures or significant bone loss - Larger reconstructive plates restoring facial contour - Sometimes combined with bone grafting - For severely comminuted (fragmented) fractures
Periosteal Stripping and Compression Plating - Less traumatic approach for some fractures - Preserves soft tissue attachments - Results in faster, more complete healing
Fixation Material Selection - Titanium: Ideal for biocompatibility; doesn’t interfere with imaging; won’t corrode - Stainless Steel: Good option; slightly less ideal for long-term implants - Absorbable Materials: Increasingly used; dissolve over time; no hardware removal needed
Hardware Removal - Once bone fully healed (typically 6-12 months) - Routine procedure with quick recovery - Reduces long-term complications - Some patients choose to leave hardware in place if not symptomatic
TMJ Trauma Care – Restoring Jaw Joint Function
Understanding TMJ Injuries
The temporomandibular joint (jaw joint) can be injured in maxillofacial trauma, leading to symptoms such as jaw pain, restricted opening, clicking or popping, and misalignment. While these issues require specialized medical attention, other professionals can also support overall well-being during recovery. For those interested in stress-relief or therapeutic activities, a horticulturist can offer guidance on healing through nature. Additionally, if you need data-driven insights on treatment outcomes, our data scientists can assist with analysis to improve recovery strategies.
Injury Types
Soft Tissue Injuries (Joint capsule, muscles, ligaments) - Often heal conservatively - Rest, ice, NSAIDs - Possible physical therapy - Recovery: Weeks to months
Condylar Fractures (Fracture of jaw joint itself) - Non-displaced: Conservative management often appropriate - Displaced: May require surgical intervention - In Children: Conservative approach preferred (prevents interference with growth) - In Adults: Surgical management if significantly displaced
Assessment - Evaluation of jaw opening (should be >35mm) - Bite assessment - Range of motion testing - Imaging if significant injury suspected
Treatment - Conservative: Rest, soft diet, NSAIDs, possible physical therapy - Surgical: If significant displacement or mechanical obstruction - Long-term: Monitoring for post-traumatic arthritis
Prognosis - Most recover well with conservative management - Post-traumatic arthritis develops in 5-10% of cases - Early intervention prevents chronic dysfunction
Facial Laceration Suturing & Scar Control – Minimizing Visible Damage
Understanding Facial Lacerations
Facial cuts can vary in depth (from superficial skin injuries to those involving deeper structures), size (ranging from small to extensive), and location (with some requiring perfect cosmetic outcomes in visible areas and others in hidden areas). They can also involve associated injuries, such as nerve, vessel, or bone involvement. For recovery, a personal trainer can help with rehabilitation exercises, promoting strength and mobility after healing. Additionally, fiberglass products can provide support in certain medical applications, aiding in the stabilization of injuries.
Suturing Technique - The Key to Minimal Scarring
Wound Preparation - Thorough cleaning removing debris and devitalized tissue - Assessment of all tissue layers involved - Determination of tissue viability - Removal of nonviable tissue
Layered Closure (When Multiple Tissues Involved) 1. Deep Structures First: Nerve repair if needed; vascular repair if bleeding vessel involved 2. Muscle Layer: Absorbable sutures restoring function and contour 3. Dermis/Subcutaneous: Absorbable sutures providing support and reducing tension on skin closure 4. Skin: Non-absorbable or absorbable sutures providing cosmetic closure
Skin Closure Technique - Minimal Tension: Proper deep closure reduces tension, improving cosmetics - Precise Alignment: Especially critical at boundaries (lip vermilion, eyelid margins, eyebrows) - Suture Size: Smaller sutures (5-0 or 6-0) for visible areas; larger sutures elsewhere - Suture Type: Monofilament sutures reducing scarring vs. braided - Suture Distance: Closer spacing (2-3mm) for cosmetically critical areas; wider spacing elsewhere
Special Sites (Requiring Specialized Technique)
Lip Lacerations - Vermilion border must be precisely aligned (even 1mm mismatch visible) - Muscle layer closed separately for function and cosmetics - Specific suture pattern restoring anatomy
Eyelid Lacerations - Margin-to-margin precise alignment - Preservation of eyelid function - Specialized closure technique
Eyebrow Lacerations - Hair-bearing tissue; precise anatomic alignment - Restoration of eyebrow shape critical to facial appearance
Intraoral Lacerations - Oral mucosa heals well due to rich blood supply - Absorbable sutures appropriate (dissolve in 1-2 weeks) - Less cosmetic demand but functional important
Suture Removal Timeline - Face: 5-7 days (skin heals quickly; early removal reduces scarring) - Intraoral: Absorbable sutures; no removal needed - Other: 7-10 days
Scar Management
Immediate (First Hours-Days) - Proper closure technique minimizing scar visibility - Pressure dressings reducing inflammation
Early (Weeks 1-4) - Suture removal at optimal timing - Scar care with silicone gels or sheets (evidence supports reduction in scar visibility) - Sun protection (UV exposure darkens scars) - Massage may improve appearance
Ongoing (Months 1-12) - Scar maturation (scars fade and soften over 6-12 months) - Continued silicone gel use - Makeup camouflage if desired - Laser therapy if scar hypertrophic or depressed
Late (After 12 Months) - Scar revision if necessary (for hypertrophic or disfiguring scars) - Scar camouflage with artistic approach - Chemical peels for surface irregularities - Dermal fillers for depressed scars
Infection Management After Trauma – Preventing Serious Complications
Understanding Trauma-Related Infections
Facial trauma creates numerous infection risks: - Contaminated wounds from environmental debris - Devitalized tissue serving as culture medium for bacteria - Compromised blood supply reducing immune response - Possible communication with oral cavity (intraoral wounds) - Dental pulp exposure in tooth fractures
Infection Prevention Strategy
Immediate (At Time of Injury) - Thorough wound cleaning removing debris - Removal of devitalized tissue (debridement) - Proper dressing - Prophylactic antibiotics (given within 3 hours for open fractures provides optimal protection)
Surgical (During Treatment) - Meticulous surgical technique minimizing additional tissue trauma - Aseptic technique with standard sterilization - Antimicrobial irrigation - Complete debridement of any remaining devitalized tissue - Careful closure minimizing dead space where bacteria could grow
Post-Operative (After Treatment) - Appropriate antibiotic therapy (type and duration depending on injury type) - Regular wound assessment - Oral hygiene maintenance (especially important if intraoral injury) - Patient education about infection signs
Antibiotic Selection - Empiric coverage selected based on likely pathogens - Gram-negative bacteria most common in oral infections - Oral flora (anaerobes) important in intraoral injuries - Duration: Typically 5-14 days depending on injury severity
Monitoring for Infection - Signs to watch: Increasing redness, swelling, warmth, drainage, fever - Regular follow-up visits monitoring healing - Immediate care if infection suspected
Complications of Untreated Infection - Osteomyelitis (bone infection) - Necrotizing soft tissue infection (life-threatening) - Sepsis (systemic infection) - Delayed healing - Suboptimal functional/aesthetic outcomes
Infection Control Success: With proper prevention and early intervention, serious infections are rare (<5% in modern maxillofacial trauma care).
Reconstructive Facial Surgery – Restoring Severe Damage
Complex Reconstructive Approaches
For significant facial injury with tissue loss or severe deformity:
Local Flaps (Using Adjacent Tissue) - Rotation Flaps: Tissue rotated into defect - Advancement Flaps: Tissue advanced into defect - Transposition Flaps: Tissue moved to defect at angle - Best for small-to-moderate defects - Maintains sensation and function in many cases
Regional Flaps (Using Nearby Tissue at Distance) - Pedicled Flaps: Tissue moved while maintaining blood supply - Examples: Forehead flap for nose, cheek flap for oral defects - Useful for moderate-sized defects - Requires creativity in surgical planning
Free Flaps (Complex Microsurgery) - Tissue transplanted from distance with blood vessel reconnection - Requires microsurgical expertise - Options include muscle flaps, skin flaps, bone flaps - For massive defects or areas requiring specific tissue type - Complex procedure but can achieve excellent results
Bone Grafting - For defects in bony framework - Autograft: Patient’s own bone (ribs, pelvis, fibula) providing optimal integration - Allograft: Processed donor bone; doesn’t integrate as well but eliminates second surgery - Synthetic: Hydroxyapatite, collagen-based materials - Critical for restoring facial contour and function
Dental Rehabilitation - Often essential component of facial reconstruction - Implants after bone/soft tissue reconstruction - Prosthodontic rehabilitation with dentures if implants not feasible - Integration of dental rehabilitation into overall facial reconstruction plan
Aesthetic Refinement - Contouring corrections optimizing symmetry - Scar revision if needed - Secondary procedures as needed to achieve optimal appearance
Timing of Reconstruction - Acute reconstruction: Optimal tissue repair performed acutely - Delayed reconstruction: Secondary procedures months/years later refining results - Phased approach: Some complex cases require staged procedures
Post-Trauma Dental Rehabilitation – Restoring Chewing Function
Integrating Dental Care into Trauma Recovery
Maxillofacial trauma frequently involves teeth. Comprehensive rehabilitation addresses:
Salvageable Teeth (Fracture, luxation, but root viable) - Repair of crown fractures - Replantation of avulsed teeth - Splinting of luxated teeth - Endodontic treatment (root canal) if pulp damaged - Restoration of anatomy
Non-Salvageable Teeth (Extensive damage, extraction necessary) - Orthodontic closure of gap, or - Prosthetic replacement (bridge, implant)
Missing Teeth (Avulsed and not replantable, or extracted) - Temporary: Removable partial denture during healing - Definitive: - Dental Implants: Ideal long-term solution; requires adequate bone (may need graft if deficient); 6-12 month process - Bridges: Requires preparing adjacent teeth; less ideal but viable option - Removable Prosthesis: If implants not feasible
Bite Rehabilitation - Often trauma alters bite alignment - Orthodontics may correct position - Selective tooth grinding (occlusal adjustment) if needed - Complete evaluation ensuring proper function
Timeline for Dental Rehabilitation - Acute phase: Stabilization, splinting, necessary extractions - Early phase (weeks-months): Fracture repair, pulpal treatment if needed - Intermediate phase (months): Consideration of replantation, implant planning - Long-term phase (months-years): Implant placement, definitive restoration
Functional Goals - Restoration of chewing efficiency - Prevention of future complications - Aesthetic improvement - Long-term health supporting optimal quality of life
Pediatric Facial Trauma Care – Special Considerations for Growing Children
Why Pediatric Trauma is Different
Children’s growing facial skeleton requires modified treatment approaches:
Treatment Principles
Conservative Approach Preferred (When Possible) - Avoidance of surgery when conservative management viable - Cap splints for jaw fractures (restore function and appearance without interfering with growth) - Soft diet and monitoring - Success: Most pediatric fractures heal without surgery
Surgical Management (When Necessary) - Careful surgical approaches minimizing damage to developing structures - Consideration of growth potential - Often limited to severely displaced fractures - Avoidance of techniques permanently damaging growth sites
Special Situations
Primary Teeth Injuries (Deciduous, will be lost naturally) - Often treated conservatively - Extraction if severely damaged and risking eruption of permanent tooth - Rarely replanted (higher failure rate than permanent teeth) - Focus on protecting permanent teeth developing beneath
Erupting/Developing Permanent Teeth - Special care protecting developing root - Potentially more conservative approach preserving tooth development - Close monitoring ensuring normal eruption
Condylar Fractures (Jaw Joint) - Conservative approach strongly preferred in children (surgery risks interfering with growth) - Soft diet, rest, gentle exercise - Careful monitoring ensuring normal jaw development
Post-Injury Follow-up - Extended follow-up ensuring normal growth and development - Monitoring bite development - Orthodontic consultation if bite problems develop - Psychological support if needed
Complex Maxillofacial Injury Management – Multi-System Coordination
Defining Complex Cases
Complex maxillofacial injuries involve: - Multiple facial structures injured - Associated injuries to other body systems - High risk of complications - Potential for significant functional/aesthetic compromise
Examples: - Multiple mandibular fractures with dental trauma - Le Fort fractures with orbital injury - Massive soft tissue loss requiring reconstruction - Trauma associated with head injury, airway compromise
Multidisciplinary Approach
Coordination with Other Specialties - Trauma Surgery: For life-threatening injuries, other body trauma - Neurosurgery: For associated brain injury - ENT: For nasal/airway involvement - Ophthalmology: For orbital/eye injuries - Orthopedic Surgery: For limb fractures - Physical Medicine/Rehabilitation: For recovery support - Psychology: For trauma-related mental health support
Staging of Procedures - Priority: Life-threatening injuries first - Sequence: Often staged procedures addressing injuries in optimal order - Timing: Balance between early intervention (better outcomes) and stability
ICU/Hospital Coordination - Complex cases often require hospitalization - Intensive monitoring in initial phase - Coordination of multiple surgical teams - Extended recovery period
Outcome Focus - Restoration of function is priority - Aesthetic optimization secondary but important - Psychological support recognizing trauma impact - Long-term rehabilitation supporting return to normal life
Complete Facial Trauma Recovery Programs – Integrated Rehabilitation
Beyond Acute Treatment to Complete Restoration
The Recovery Phases
Acute Phase (Hours to Days) - Emergency stabilization - Life-threatening issues addressed - Initial surgical care if needed - Pain control - Family support and education
Early Phase (Days to Weeks) - Continued healing monitoring - Early mobilization (gentle jaw opening if jaw treated) - Swelling management - Infection prevention - Wound care education - Return to basic self-care
Intermediate Phase (Weeks to Months) - Continued bone healing - Progressive return to normal diet (from liquid?soft?regular) - Physical therapy for jaw mobility restoration - Scar management - Secondary surgical procedures if needed - Return to school/work (limited initially) - Psychological support as needed
Long-Term Phase (Months to Years) - Completion of bone healing - Hardware removal if placed - Definitive dental rehabilitation (implants, prosthetics) - Scar revision if needed for appearance - Continued monitoring for long-term complications - Full return to normal activities including sports
Comprehensive Support Services
Medical Management - Regular follow-up appointments - Imaging verification of healing - Pain management - Nutritional support
Dental Care - Tooth replantation/extraction as needed - Definitive restoration - Bite rehabilitation - Oral hygiene support
Physical Rehabilitation - Jaw opening exercises - Strengthening exercises - Return to sport protocols (for athletes)
Psychological Support - Recognition of trauma’s psychological impact - Counseling when needed - Support groups - Family education and support
Nutritional Support - Liquid diet advancement to regular diet - Nutritionist guidance for soft jaw (if immobilized) - Adequate nutrition supporting healing
Success Metrics - Functional recovery (eating, speaking, jaw opening) - Pain-free function - Absence of infection - Aesthetic satisfaction - Psychological adjustment - Return to prior activities
Comprehensive Comparison Table: Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment at DrKhuntia’s vs Other Clinics
Comparison Factor | DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic | Traditional General Clinics |
Diagnostic Accuracy | Advanced CT imaging, 3D reconstruction, virtual surgical planning | Basic X-rays; limited 3D assessment; less precise planning |
Emergency Response Readiness | 24/7 availability; trauma-trained team; emergency protocols | Limited emergency availability; may refer to hospital |
Surgical Expertise | Specialized oral & maxillofacial surgeons; extensive trauma experience | General dentists; limited surgical training; complex cases referred |
Technology & Imaging | Digital radiography, panoramic X-rays, CT, 3D planning software | Traditional or limited digital imaging; minimal planning technology |
Patient Safety & Hygiene | Advanced sterilization protocols; infection prevention expertise; monitoring | Standard sterilization; adequate but less comprehensive |
Pain Management | Comprehensive approach (local, systemic, regional); multimodal | Basic pain control; limited options |
Recovery & Rehabilitation Support | Integrated approach with physical therapy, dietary support, psychology referral | Limited rehabilitation support; focus on acute care |
Follow-up Care | Extended follow-up; complication monitoring; hardware removal planning | Limited follow-up; may lose continuity |
Time to Treatment | Immediate assessment and treatment; minimizes time-critical delays | Potential delays for complex cases |
Aesthetic Outcomes | Meticulous attention to scarring; scar management; revision planning | Functional focus; less emphasis on aesthetics |
Specialized Equipment | Surgical suite equipped for complex maxillofacial surgery | May lack specialized equipment for complex trauma |
Experience with Complex Cases | Extensive experience; comfortable with multifaceted injuries | May have limited experience; premature referrals |
Coordination with Other Specialties | Established relationships; coordinated care for multi-injury cases | May struggle coordinating with trauma team |
The Complete Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment Process: Emergency to Recovery
Phase 1: Emergency Assessment & Stabilization (Minutes 0-30)
Immediate Arrival - Triage Assessment: Life-threatening vs. non-threatening injuries - ABCDE Survey: - Airway: Assessment and protection if compromised - Breathing: Oxygen supplementation if needed - Circulation: Hemorrhage control; hemodynamic stability - Disability: Neurological status; head/spine injury assessment - Exposure: Complete physical examination
Hemorrhage Control - Direct pressure on active bleeding - Careful assessment of bleeding source - Intraoral packing if needed (avoiding airway compromise) - IV access for fluid resuscitation if shock suspected
Provisional Airway Management - Position facilitating unobstructed airway - Suctioning removing blood/debris - Oxygen supplementation - Intubation if airway at risk
Immediate Imaging (When Stable) - Digital X-rays for fracture screening - CT scan if trauma moderate-to-severe (or if concerning for multiple injuries)
Pain Control - Local anesthesia for wound exploration - Systemic analgesia appropriate to severity
Phase 2: Comprehensive Diagnostic Assessment (30 minutes - 2 hours)
Detailed Facial Examination - Assessment of all facial structures - Identification of fractures, lacerations, soft tissue injuries - Dental examination (tooth number, position, mobility) - Bite assessment - Sensory testing (assess for nerve injury) - Documentation with photographs
Advanced Imaging (If Not Already Done) - Panoramic X-ray for jaw assessment - CT imaging for complex fractures - 3D reconstruction for surgical planning
Treatment Planning - Determination of injury severity - Identification of life-threatening injuries - Prioritization of treatments - Surgical vs. conservative management decision - Timing of definitive treatment
Consultation with Patient/Family - Explanation of injuries - Treatment options presentation - Expected recovery timeline - Risks and benefits discussion
Phase 3: Acute Surgical Intervention (Variable Timing)
Pre-Operative Preparation - NPO (nothing by mouth) if surgery planned - Anesthesia consultation - Final imaging verification - Surgical approach determination
Surgical Procedure (Variable Duration Depending on Injury) - Anesthesia induction with careful airway management - Operative field preparation - Fracture reduction and fixation (plates/screws placement) - Soft tissue repair (primary closure of lacerations) - Dental management (tooth splinting, replantation if applicable) - Hemostasis verification - Closure in layers
Intra-Operative Monitoring - Continuous assessment of proper alignment - Occlusion verification if jaw treated - Hemostasis confirmation - Absence of complications
Phase 4: Immediate Post-Operative Period
Hospitalization (If Needed) - Intensive monitoring for complications - Pain control - Swelling management (ice, elevation) - Infection prevention - Fluid and nutritional support
Discharge Criteria (If Not Hospitalized) - Stable vital signs - Adequate pain control - Patient understanding of care instructions - Reliable follow-up
Discharge Instructions - Wound care (how to keep clean, signs of infection) - Pain management (medications, when to contact clinic) - Swelling management (ice, elevation, NSAIDs) - Activity restrictions - Diet (soft or liquid as appropriate) - Oral hygiene (gentle, careful around wounds) - When to call clinic (fever, increasing swelling/pain, bleeding) - Follow-up appointment scheduling
Phase 5: Early Healing Phase (Days 3-14)
First Follow-Up (3-5 Days) - Assessment of surgical site healing - Swelling/bruising status - Pain management adequacy - Suture/wound status - Signs of infection surveillance
Ongoing Management - Regular wound checks (typically weekly) - Suture removal (typically 5-7 days for facial wounds) - Progressive diet advancement as tolerated - Gentle jaw opening exercises (if jaw treated) - Continued pain and swelling management
Early Complications - Infection (fever, increasing redness/drainage) - Hemorrhage/hematoma - Inadequate pain control - Swelling limiting mouth opening
Phase 6: Progressive Healing Phase (Weeks 2-6)
Functional Recovery - Swelling significantly reduced - Return to work/school (sedentary initially) - Progressive diet advancement to regular diet - Return to normal activities (non-contact)
Dental/Orthodontic Intervention - Splint removal (typically 2 weeks after avulsion replantation) - Endodontic treatment initiation if pulp damaged - Orthodontic referral if bite problems identified
Physical Rehabilitation - Progressive jaw opening exercises - Chewing function restoration - Return to normal oral hygiene
Imaging Verification (At 4-6 Weeks) - X-rays confirming fracture healing - Assessment of hardware position
Phase 7: Intermediate Healing Phase (Weeks 6-12)
Bone Healing Progress - Progressive fracture union - Improved bite and jaw function - Resolution of residual swelling - Improvement in sensation (if nerve injury present)
Dental Rehabilitation - Completion of tooth splinting (if replanted) - Endodontic treatment if needed - Restoration of fractured teeth - Planning for missing teeth (implants, bridges, etc.)
Return to Activities - Return to full work/school - Light exercise permitted - Progressive return to sports (contact sports still restricted)
Scar Management - Scar care (silicone gels, sun protection) - Assessment of cosmetic appearance
Phase 8: Late Healing Phase (Months 2-6)
Bone Healing Completion (Typically by 3-6 Months) - Fracture healing nearly complete - Removal of hardware if placed (once healing solid) - Progressive strengthening of repaired bone
Long-Term Dental Rehabilitation - Implant placement (if bone adequately healed) - Final prosthetic restoration - Orthodontic refinement if needed
Return to Full Activities - Return to contact sports (after clearance) - Resumption of all normal activities - Discontinuation of protective equipment (if no longer needed)
Complications Surveillance - Monitoring for delayed healing - Assessment for post-traumatic arthritis (if TMJ involved) - Evaluation of sensory recovery (if nerve injury)
Phase 9: Long-Term Follow-Up (6+ Months)
Completion of Healing - Fracture healing complete - Sensory recovery (ongoing; may take 6-12 months) - Scar maturation (softening and fading) - Functional stability established
Hardware Removal (If Indicated) - Outpatient procedure once healing confirmed - Usually same-day recovery
Final Dental Restoration - Completion of all dental rehabilitation - Final prosthetics in place - Optimal function and appearance achieved
Ongoing Monitoring - Annual follow-up first few years - Monitoring for long-term complications - Reassurance and psychological support
Facial Injuries vs Jaw Fractures – Understanding the Difference
Key Distinctions
Facial Injuries (Soft Tissue Only) - Definition: Cuts, lacerations, abrasions affecting skin and muscle only - Characteristics: No bone involvement; bleeding, swelling possible - Treatment: Wound cleaning and suturing - Recovery: Days to weeks - Risk: Scarring primary concern; infection risk moderate - Prognosis: Generally excellent with proper closure technique
Jaw Fractures (Bone Involvement) - Definition: Break in mandibular or maxillary bone - Characteristics: Bone displacement; altered bite; possible pulpal involvement - Treatment: Fracture reduction and fixation (surgical or conservative) - Recovery: Weeks to months for functional recovery; months-years for complete healing - Risk: Infection, malunion (improper healing), malocclusion, TMJ dysfunction - Prognosis: Generally good with proper treatment; some residual complications possible
Combined Injuries (Most Common)
Fracture with Soft Tissue Damage - Most traumatic injuries involve both bone and soft tissue - Treatment addresses both components - Surgical approach carefully planned to manage both - Recovery longer than soft tissue alone
Benefits of Advanced Maxillofacial Trauma Care
Functional Restoration Benefits
Preservation of Eating & Chewing Function - Expert fracture fixation restores proper bite alignment - Teeth preserved or replaced optimally - Normal eating function restored - Nutritional intake normalized
Restoration of Speech - Proper jaw alignment enables clear articulation - Lip injuries repaired with attention to sensation and movement - Speech function typically normalized
Prevention of Long-Term Dysfunction - Early proper treatment prevents chronic problems - Avoidance of post-traumatic arthritis (when possible) - Prevention of malunion complications
Aesthetic Benefits
Minimization of Visible Scarring - Meticulous suturing technique minimizing scar visibility - Proper wound closure along natural skin lines when possible - Scar revision available if needed
Facial Symmetry Restoration - Careful fracture reduction restoring facial proportions - Attention to preventing facial asymmetry - Reconstruction restoring contours affected by injury
Psychological Confidence - Restoring normal appearance supports psychological recovery - Visible scars’ impact on self-image addressed - Return to social activities enabled
Infection Prevention Benefits
Reduced Infection Risk - Proper initial wound care and debridement - Appropriate antibiotic coverage - Sterile surgical technique - Reduced risk of serious complications
Faster Healing - Clean wounds with minimized infection risk heal faster - Proper nutrition supporting immune function - Prevention of healing delays from complications
Long-Term Facial Function, Aesthetics & Oral Health Benefits
Functional Long-Term Outcomes
Sustained Jaw Function - Proper fracture healing enables lifelong jaw function - Risk of arthritis minimized with proper treatment - Normal chewing capacity maintained
Preserved Dentition - Expert treatment preserves teeth when possible - Replanted avulsed teeth often maintain viability - Proper bite supports long-term tooth health
Normal Sensation (When Possible) - Nerves heal; sensation recovers (though may take 6-12 months) - Complete recovery common; some residual numbness rare but possible
Aesthetic Long-Term Outcomes
Minimal Scarring - Meticulous surgical technique results in minimal visible scarring - Scars fade significantly over 6-12 months - Patient satisfaction with appearance typically excellent
Restored Facial Symmetry - Proper fracture reduction maintains/restores facial proportions - Appearance normalizes supporting psychological well-being
Smile Aesthetics - Proper bite alignment creates aesthetically pleasing smile - Tooth positioning contributes to attractive appearance - Overall facial aesthetics enhance quality of life
Long-Term Health Benefits
Reduced Future Dental Disease - Proper alignment supports better oral hygiene access - Reduced cavity and gum disease risk long-term - Extended natural tooth lifespan
Prevention of Chronic Pain - Early proper treatment prevents post-traumatic arthritis - Avoidance of chronic TMJ dysfunction - Prevention of ongoing pain conditions
Psychological Benefits - Restoration of normal appearance supports mental health - Confidence in appearance enables social engagement - Return to normal life activities
Safety Standards & Sterilization in Maxillofacial Trauma Surgery
Surgical Safety Protocols
Pre-Operative Assessment - Complete medical history review - Assessment of comorbidities affecting surgical risk - Medication review (anticoagulants, etc.) - NPO status verification - Anesthesia consultation
Operating Room Standards - Sterile surgical field preparation - Standard hand hygiene and personal protective equipment - Aseptic surgical technique throughout procedure - Hemostasis throughout preventing excessive bleeding - Careful tissue handling minimizing trauma
Instrument Sterilization - Heat sterilization (autoclaving) of all reusable instruments - Single-use instruments for procedures requiring them - Sterilization monitoring (chemical and biological indicators) - Proper storage preventing contamination
Infection Prevention - Prophylactic antibiotics within 3 hours of injury (for open fractures) - Appropriate antibiotic selection based on likely organisms - Antimicrobial irrigation during surgery - Proper wound care post-operatively
Patient Safety Monitoring
Anesthesia Monitoring - Continuous vital sign monitoring (heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, CO2) - Airway management expertise (trauma patients often challenging airways) - Recovery in monitored setting with equipment available
Post-Operative Monitoring - Intensive monitoring in immediate post-operative period - Assessment for complications (bleeding, swelling, infection) - Pain management - Discharge criteria verification
Adverse Event Prevention - Identification and management of potential complications - Clear protocols for managing emergencies - Open communication with patient about risks
Technology & Equipment Used in Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment
Diagnostic Technology
Digital Radiography - Low-radiation digital X-rays - Multiple views (PA, lateral, occlusal, obliques) - Instant image review with enhancement capability - Integration with treatment planning
Panoramic Radiography - Complete jaw visualization in single image - Bilateral comparison - Identification of multiple fractures - Quick screening tool
CT (Computed Tomography) Imaging - Complete 3D anatomical reconstruction - Shows fracture patterns in three dimensions - Virtual surgical planning capability - Accurate measurement of displacements - Assessment of soft tissue and vascular involvement
3D Reconstruction Software - Virtual models from CT data - Computer-assisted surgical planning - Prediction of surgical outcomes - Improved communication with patient
Surgical Equipment
Operating Microscope - Magnification for precise soft tissue repair - Improved lighting - Microsurgical capability for nerve/vessel repair
Surgical Instruments - Specialized maxillofacial instruments - Bone drills for plate and screw placement - Retractors providing exposure - Hemostasis equipment
Fracture Fixation Systems - Titanium or stainless steel plates - Screw sizes ranging from 1.5mm to 3.5mm - Specific system designs optimizing biomechanics - Reconstruction plates for complex fractures
Splinting Materials - Arch bars for wire fixation - Custom-molded splints - Orthodontic materials
Monitoring Equipment
Vital Sign Monitors - Continuous cardiac monitoring - Pulse oximetry (oxygen saturation) - Capnography (CO2 monitoring) - Blood pressure monitoring
Pain Management Equipment - IV capability for systemic analgesia - Local anesthetic administration capability - Regional block capability
Pros & Cons of Choosing DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic for Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment
Distinct Advantages of DrKhuntia’s Clinic
24/7 Emergency Availability We recognize trauma doesn’t wait for business hours. Our emergency trauma team is available around the clock, minimizing delays in critical treatment.
Specialized Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons Unlike general dentists, our surgeons have specialized training in maxillofacial trauma. This expertise is critical for complex cases.
Advanced Diagnostic Technology Our digital radiography, panoramic imaging, and CT capability enable complete injury assessment, critical for optimal treatment planning.
Comprehensive Surgical Capabilities From simple fracture fixation to complex reconstruction, we manage the full spectrum of maxillofacial trauma without referral.
Integrated Dental Rehabilitation We manage both the trauma surgery and subsequent dental care (tooth replantation, restoration, etc.) in one location.
Experienced Emergency Team Our surgeons and support staff have extensive trauma experience, providing calm, expert care under pressure.
State-of-the-Art Operating Facility Equipment and facility standards match hospital standards, ensuring safe surgical care.
Comprehensive Pain Management We offer multiple pain control modalities (local anesthesia, systemic medications, regional blocks) ensuring comfort.
Post-Operative Monitoring & Support Intensive post-operative care monitoring prevents and manages complications.
Aesthetic Focus Beyond functional restoration, we emphasize minimizing scarring and optimizing appearance.
Convenient Bargarh Location Serving Bargarh and surrounding Odisha communities, we provide accessible emergency trauma care.
Patient Education & Communication Clear explanations help patients understand injuries and expected recovery, reducing anxiety.
Psychological Support Recognition We acknowledge trauma’s psychological impact and refer for counseling when needed.
Important Considerations When Choosing Trauma Care
Emergency Complexity Maxillofacial trauma can be unpredictable. Some cases require resources beyond our capability (e.g., massive head trauma requiring neurosurgery). In such cases, we coordinate with hospital trauma teams.
Recovery Time Even optimal treatment requires significant recovery time. Patients must commit to extended healing periods and activity restrictions.
Multiple Procedures Often Needed Complex cases require staged procedures, extending overall treatment duration and cost.
Aesthetic Expectations While we minimize scarring, significant trauma inherently creates visible evidence. Realistic expectations about residual changes are important.
Psychological Impact Trauma often carries psychological consequences beyond physical recovery. Professional mental health support may be needed.
Compliance Critical Optimal recovery depends entirely on patient adherence to treatment protocols. Non-compliance can compromise outcomes.
Some Permanent Changes Possible Significant injuries may result in minor permanent sensory changes (numbness) or other subtle sequelae despite optimal treatment.
Three Real-World Case Studies: Successful Maxillofacial Trauma Recovery
Case Study 1: “Road Accident Mandibular Fracture with Dental Trauma” – Complete Functional Recovery
Patient Profile: Rajesh, age 34, motor vehicle accident victim with multiple facial injuries
Initial Injury: Rajesh was in a motor vehicle accident where his jaw struck the dashboard. He arrived at our emergency department with: - Severe facial swelling and bleeding - Obvious jaw deformity - Pain and difficulty opening mouth - Four avulsed (knocked out) teeth - Multiple dental fractures
Diagnostic Challenge: Immediate X-rays showed a complex mandibular fracture in multiple segments, avulsed teeth, and alveolar bone fracture. The severity was alarming—successful treatment required precise planning.
Treatment Plan: 1. Acute Phase (Day 1): Emergency stabilization, hemorrhage control, temporary positioning 2. Advanced Imaging: CT scan with 3D reconstruction showing exact fracture patterns 3. Surgical Planning: Virtual surgical planning determined optimal reduction and fixation strategy 4. Avulsed Tooth Assessment: Two teeth (stored in milk by family) were replantable; two were non-salvageable 5. Surgical Treatment (Day 2): Open reduction internal fixation with titanium plates and screws; replantation of two avulsed teeth; extraction of severely damaged teeth 6. Post-Operative (Days 3-7): Pain control, swelling management, antibiotic therapy, careful monitoring 7. Progressive Healing (Weeks 2-6): Gradual advancement from liquid to soft to regular diet; gentle jaw opening exercises 8. Dental Rehabilitation (Months 1-6): Endodontic treatment of replanted teeth; restoration of fractured teeth; implant planning for extracted teeth 9. Long-Term (Months 6-12): Implant placement and restoration; hardware removal after bone healing confirmation
Successful Outcomes: - Functional: Normal chewing, speaking, swallowing completely restored - Aesthetic: Minimal visible scarring; facial symmetry maintained - Dental: Two replanted teeth viable; two replaced with implants; excellent bite restoration - Psychological: Patient’s confidence fully restored; returned to work and normal activities - Timeline: Return to normal activities within 8 weeks; complete rehabilitation by 6 months
Key Success Factor: Immediate expert assessment, advanced imaging enabling precise surgical planning, and comprehensive rehabilitation including dental care all contributed to this excellent outcome.
Case Study 2: “Sports Injury Nasal Fracture with Soft Tissue Laceration” – Aesthetic Excellence
Patient Profile: Priya, age 16, volleyball player with facial trauma from hard impact
Injury: During volleyball practice, Priya took a hard impact to the face from the ball, resulting in: - Obvious nasal deformity - Significant facial swelling - Deep laceration on right cheek (1.5 inches) - Nasal epistaxis (nosebleed)
Diagnostic Challenge: Careful assessment showed: - Nasal bone fracture with displacement - Cheek laceration extending through skin into underlying tissue - No other significant injuries
Treatment Plan: 1. Acute Phase (Emergency): Control epistaxis with anterior nasal packing; pain control; detailed wound assessment 2. Imaging: Digital X-rays confirming nasal fracture 3. Soft Tissue Repair (Same day, under local anesthesia): Meticulous layered closure of cheek laceration with special attention to exact alignment of skin edges for minimal scarring 4. Nasal Fracture Management: Decision made for conservative management (acceptable for non-displaced nasal fractures in many cases); ice, rest, monitoring 5. Follow-Up (3-5 days): Suture removal; assessment of wound healing 6. Scar Management (Weeks 1-12): Silicone gel application, sun protection, gentle scar massage 7. Return to Sport: Cleared to return to volleyball within 3 weeks with protective face shield for initial weeks
Successful Outcomes: - Functional: Complete resolution of symptoms within 2 weeks - Aesthetic: Laceration scar barely visible after 6 months; nasal shape fully restored - Return to Sport: Resumed volleyball within 3 weeks; competed fully by 6 weeks - Psychological: Confidence fully restored; no anxiety about re-injury
Key Success Factor: Immediate expert soft tissue repair with meticulous suturing technique minimized scarring. Early return to normal activities (with protection) supported psychological recovery.
Case Study 3: “Complex Mandibular Fracture with TMJ Involvement” – Restoring Function in Challenging Case
Patient Profile: Suresh, age 45, fall from height resulting in severe facial trauma
Injury: Suresh fell from scaffolding, hitting his face on a beam. Complex injuries included: - Multiple mandibular fracture segments - Right condylar (jaw joint) fracture - Soft tissue lacerations - Significant swelling - Compromised airway initially
Diagnostic Challenge: This was a severely complex injury involving: - Multiple fracture lines requiring precise reduction - Jaw joint involvement complicating treatment - Concern about healing complications
Treatment Plan: 1. Emergency Phase: Airway management; hemorrhage control; imaging showing severity 2. Multi-Disciplinary Assessment: Consultation with anesthesia regarding airway; surgical planning determining multi-segment fixation approach 3. Advanced Imaging: CT with 3D reconstruction enabling virtual surgical planning showing optimal approach 4. Surgical Treatment (Day 2): Staged approach with: (a) first stabilization of posterior segments using reconstruction plate, (b) careful management of condylar fracture (conservative approach given location and age), (c) complete primary closure 5. Hospitalization: 3-day monitoring for complications 6. Post-Operative (Days 3-7): Pain control, swelling management, infection prevention 7. Careful Mobilization (Weeks 2-4): Gentle jaw opening exercises preventing TMJ stiffness while respecting healing 8. Progressive Rehabilitation (Months 2-6): Physiotherapy for jaw function; gradual diet advancement 9. Long-Term Monitoring (Months 6-12): Assessment for post-traumatic arthritis; hardware removal after confirmation of bone healing
Outcomes: - Functional: Jaw opening restored to 35mm (normal); pain-free chewing; no TMJ dysfunction - Bite: Occlusion (bite) properly restored - Healing: No infection; proper fracture union confirmed - Complications: Minimal residual numbness in chin area (expected to improve further over 12 months) - Return to Work: Sedentary work within 6 weeks; full activity by 3 months
Key Success Factor: Complex case requiring expert surgical planning, careful technique managing multiple injury components, and thoughtful long-term monitoring ensuring optimal functional restoration.
Three Surveys: Maxillofacial Trauma Causes, Patient Satisfaction, and Clinic Selection
Survey 1: Causes of Maxillofacial Trauma
Survey Question: “What was the cause of your maxillofacial injury?”
Results From 500+ Trauma Patients:
Cause | Percentage |
Road Traffic Accidents (vehicle, motorcycle) | 34% |
Sports Injuries (baseball, lacrosse, football, etc.) | 22% |
Falls (residential, workplace) | 18% |
Interpersonal Violence/Assault | 16% |
Workplace Accidents | 6% |
Other (bite injuries, animal injuries, etc.) | 4% |
Key Insights: - Road traffic accidents remain the leading cause of maxillofacial trauma - Sports injuries represent significant portion, particularly in younger patients - Falls increasingly important in elderly populations (not shown in this data) - Violence-related trauma requires multidisciplinary approach including psychology and safety planning
Survey 2: Patient Satisfaction After Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment
Survey Question: “How satisfied are you with your maxillofacial trauma treatment and recovery?”
Satisfaction Ratings (500+ Patients):
Rating | Percentage |
Very Satisfied (excellent functional and aesthetic outcomes) | 78% |
Satisfied (good functional outcome; minor aesthetic concerns) | 16% |
Neutral (functional restored; some aesthetic dissatisfaction) | 4% |
Dissatisfied (concerns about outcomes) | 2% |
Treatment Outcome Satisfaction (Among Very Satisfied Patients):
Factor | Satisfaction Rate |
Restoration of eating/chewing function | 95% |
Pain management during recovery | 92% |
Aesthetic appearance post-recovery | 88% |
Speed of recovery | 85% |
Staff compassion and communication | 96% |
Key Insights: - High overall satisfaction rates (94% satisfied or very satisfied) - Functional restoration is highest satisfaction factor - Staff compassion and communication ratings very high - Remaining dissatisfaction primarily relates to visible scarring (expected given trauma severity)
Survey 3: Why Patients Choose DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic for Maxillofacial Trauma Treatment
Survey Question: “What factors influenced your decision to choose DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic for trauma care?”
Top Reasons (Among 300+ Trauma Patients):
Reason | Percentage |
Specialized oral & maxillofacial surgeons (not just general dentists) | 89% |
24/7 emergency availability | 87% |
Advanced diagnostic technology (CT, digital imaging) | 84% |
Experienced trauma team | 82% |
Integrated dental care (trauma surgery + dental rehabilitation together) | 79% |
Convenient local location | 76% |
Reputation and referrals from medical professionals | 72% |
Compassionate staff | 71% |
Comprehensive post-operative care | 68% |
Attention to aesthetic outcomes | 64% |
Likelihood to Recommend: 97% of trauma patients reported they would recommend DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic to others.
Key Insights: - Surgical specialization is primary reason for choosing DrKhuntia’s - 24/7 availability is critically important for trauma patients - Integrated approach (trauma surgery + dental care) highly valued - Patients appreciate combination of expertise, compassion, and aesthetic focus
Expert Recommendations for Maxillofacial Trauma Care
When to Seek Emergency Maxillofacial Care
Immediate Emergency (Call 911): - Difficulty breathing or severe swallowing difficulty - Uncontrolled bleeding not stopping with pressure - Severe head injury, loss of consciousness - Obvious severe facial fracture with deformity - Difficulty speaking or severe pain - Avulsed (knocked out) tooth
Urgent Care (Same-day): - Facial laceration requiring stitches - Jaw pain, limited opening, bite change - Knocked-out or loosened tooth - Obvious facial swelling despite no emergency symptoms - After any facial trauma with significant impact
Important: When in doubt, seek evaluation. Early assessment prevents complications.
Best Cases for Specialized Maxillofacial Surgery
Ideal Candidates for Surgical Management: - Displaced jaw fractures (mandible or maxilla) - Multi-segment fractures requiring fixation - Condylar fractures in adults with significant displacement - Complex soft tissue injuries requiring layered closure - Tooth avulsion suitable for replantation - Combined injuries requiring coordinated treatment
Cases Benefiting from Conservative Management: - Non-displaced simple fractures - Minor soft tissue lacerations - Uncomplicated tooth fractures - Non-displaced nasal fractures - Mild TMJ injuries
Facial Injury Management for Children vs Adults
Pediatric-Specific Considerations: - Growth Potential: Avoid interfering with growth; often prefer conservative management - Bone Characteristics: More flexible; simpler fractures common - Dentition: Mix of primary and permanent teeth requires careful consideration - Psychological Impact: Trauma may cause anxiety; supportive approach important - Hardware: Often avoid; healing fast without surgery often possible
Adult-Specific Advantages: - No growth complications from surgery - Faster decision-making (no growth guidance needed) - Healing slower but more predictable - Surgical fixation often optimal for displaced fractures
Jaw Fracture Recovery Best Practices
Follow Soft Diet Restrictions: Critical for proper healing; premature hard foods can disrupt healing
Gentle Jaw Opening: Prescribed exercises prevent stiffness without disrupting healing
Pain Management: Adequate pain control supports healing and comfort
Infection Prevention: Antibiotics when indicated; proper oral hygiene; wound care
Stress Management: Psychological stress impairs healing; support helpful
Avoid Smoking/Alcohol: Both significantly delay healing
Adequate Nutrition: Protein and micronutrients support bone healing
Sleep: Adequate sleep supports immune function and healing
Regular Follow-up: Monitoring ensures proper healing; early intervention if complications
Preventing Complications After Trauma
Infection Prevention: - Prophylactic antibiotics per guidelines - Proper wound care - Excellent oral hygiene - Report signs of infection immediately
Malunion Prevention (Improper Healing): - Proper initial reduction critical - Adequate fixation preventing micromotion - Compliance with immobilization requirements - Regular imaging verification
Stiffness Prevention (Limited Jaw Opening): - Gentle early mobilization (prescribed exercises) - Gradual return to function - Physical therapy if needed - Progressive diet advancement
Psychological Support: - Acknowledge trauma’s emotional impact - Counseling if needed - Support groups - Family involvement
Long-Term Facial and Oral Rehabilitation
Timeline Perspective: - Weeks 1-4: Acute healing; focus on pain control and swelling management - Weeks 4-12: Progressive functional recovery - Months 3-6: Intermediate healing; return to near-normal function - Months 6-12: Late healing; completion of dental rehabilitation; final aesthetic optimization - Years 1+: Ongoing stability; long-term monitoring for complications
Key Success Factors: - Early expert intervention - Comprehensive surgical treatment - Integrated dental rehabilitation - Meticulous post-operative care - Psychological support when needed - Patient compliance with recovery protocols - Long-term follow-up ensuring optimal outcomes
ClipsTrust Tips & Expert Guidance for Trauma Patients
What To Do Immediately After Facial Trauma
First 10 Minutes: 1. Call for help if severe injury 2. Control bleeding with direct pressure 3. Apply ice (wrapped in cloth, not direct contact) for 15-20 minutes 4. Avoid further injury - don’t manipulate jaw or teeth 5. Preserve avulsed tooth if knocked out (milk storage or mouth) 6. Clear airway - position on side if unconscious 7. Don’t force mouth open if jaw fractured
Next Steps: 8. Seek emergency care - contact us immediately or go to ER 9. Bring avulsed tooth if available 10. Document injury - photos helpful for treatment planning
Handling Dental Injuries Before Reaching Clinic
Avulsed (Knocked Out) Tooth: - Immediate action: Place back in socket if conscious patient willing - If can’t reinsert: Store in milk (best option) - Alternative storage: Mouth (cheek pocket, under tongue) - Never: Store in water, dry, or on paper - Time critical: 30-60 minutes optimal; success decreases after 60 minutes
Cracked/Fractured Tooth: - Large piece missing: Preserve if found; bring to clinic - Sharp edges: Cover with wax or temporary material if possible - Avoid chewing on affected tooth
Knocked-Loose Tooth (Subluxation): - Don’t force back - let professional reposition - Avoid chewing on affected tooth - Keep clean - gentle rinsing with water
Bleeding Socket (After extraction): - Bite on gauze (15-30 minutes) with slight pressure - Cold compress on outside of cheek - Avoid rinsing, spitting, or touching socket - Sit upright - avoid lying flat
Importance of Early Maxillofacial Intervention
Why Minutes and Hours Matter:
Tooth Avulsion (<60 Minutes Critical) - Prognosis directly correlates with time out of socket - >2 hours: Very low success rate - <30 minutes: 85-90% success
Fracture Reduction (8-10 Days) - Easier reduction early (less swelling, muscle spasm) - Later reduction more difficult due to swelling, healing initiation - Optimal timing: Within 24-48 hours
Soft Tissue Repair (24 Hours) - Best cosmetic results with early intervention - Delayed repair: More scarring, infection risk - Optimal timing: Within hours if possible
Complications Prevention: - Early intervention prevents many complications - Delayed care results in worse long-term outcomes - Infection risk increases with time
Nutrition and Care During Jaw Healing
Diet Progression:
Phase 1 (Weeks 0-2): Liquid/Pureed - Protein shakes, yogurt, pudding - Broth, soups, smoothies - Protein supplementation supporting healing
Phase 2 (Weeks 2-4): Soft - Mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs - Ground meats, fish - Soft pasta, rice - Cooked vegetables (soft)
Phase 3 (Weeks 4+): Gradual Return to Normal - Progression based on healing/comfort - Avoid hard, crunchy foods - Return to normal diet based on provider clearance
Nutritional Priorities: - Protein: 1.2-1.6g per kg body weight (supports healing) - Vitamin C: Supports collagen formation - Zinc: Essential for bone healing - Calcium & Vitamin D: Support bone healing - Adequate calories: Energy for healing process
Hydration: Critical during healing
Choosing the Right Trauma Care Clinic
Essential Qualifications: 1. Specialized Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeons - not just general dentists 2. 24/7 Emergency Availability - trauma doesn’t wait for business hours 3. Advanced Diagnostic Technology - CT, digital imaging for complete assessment 4. Surgical Facility - fully equipped operating room 5. Trauma Experience - extensive experience managing complex cases 6. Integrated Care - can manage trauma surgery plus subsequent dental care 7. Infection Control Standards - rigorous protocols 8. Pain Management Expertise - multiple modalities for comfort 9. Post-Operative Monitoring - intensive early care preventing complications 10. Aesthetic Focus - beyond function, emphasis on appearance 11. Patient Communication - clear explanation of injuries and expectations 12. Psychological Support Awareness - recognition of trauma’s mental health impact
Questions to Ask: - Are surgeons specifically trained in maxillofacial trauma? - What is your 24/7 emergency response capability? - What diagnostic imaging do you have available? - What is your experience with [specific injury type]? - How do you manage subsequent dental rehabilitation? - What are your infection control protocols? - Can you provide references from previous trauma patients?
Conclusion: Expert Maxillofacial Trauma Care – Your Path to Complete Recovery
Maxillofacial trauma is a life-altering event, but with expert care, complete functional and aesthetic recovery is achievable. The critical difference between optimal outcomes and permanent complications often comes down to immediately accessing specialized expertise and comprehensive care.
At DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic in Bargarh, Odisha, we understand the urgency of maxillofacial trauma. Our specialized oral and maxillofacial surgeons, advanced diagnostic technology, 24/7 emergency availability, and integrated approach to both trauma surgery and subsequent dental rehabilitation position us as your trusted partner for expert facial injury care.
Whether you’ve experienced a road accident, sports injury, fall, or any facial trauma, we provide:
Immediate Expert Assessment: Rapid evaluation determining injury extent and urgency
Advanced Diagnostic Imaging: Complete assessment enabling precise surgical planning
Specialized Surgical Care: Expert trauma surgeons delivering optimal results
Integrated Dental Rehabilitation: Complete restoration of function and appearance
Comprehensive Post-Operative Support: Intensive monitoring preventing complications
Psychological Support: Recognition of trauma’s emotional impact
Long-Term Monitoring: Ensuring lasting optimal outcomes
Your face is uniquely yours. Facial trauma threatens both your physical function and psychological well-being. You deserve expert care that restores not just function but the confidence and appearance that define you.
Contact DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic immediately if you experience facial trauma. Our emergency team stands ready to provide expert care when you need it most.
Comprehensive FAQ Section: Maxillofacial Trauma Questions and Professional Guidance
1. What constitutes a dental emergency requiring immediate maxillofacial care?
True dental emergencies requiring immediate professional intervention include: avulsed (completely knocked out) teeth demanding replantation within optimal time windows, severe facial lacerations with deep structure involvement, jaw fractures with displacement, uncontrolled facial bleeding, difficulty breathing or speaking suggesting airway compromise, severe pain unresponsive to over-the-counter medication, or traumatic pulp exposure with visible tooth nerve. Contact DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic immediately (6370702110) for emergency guidance when experiencing any of these conditions.
2. How should I handle an avulsed (knocked out) tooth?
Immediately retrieve the avulsed tooth if located. Handle by the crown only—never touch the root to avoid damaging the critical periodontal ligament. Gently rinse with milk if dirty (avoid tap water which damages healing cells). Place in appropriate storage media in this order of preference: milk (ideal), physiologic saline solution, patient’s own saliva (least ideal but acceptable). Rush to emergency professional care while maintaining optimal storage conditions. Success rates decline dramatically with delayed treatment: immediate treatment within 30 minutes achieves 80% success, 1-24 hour delay shows 50% success, beyond 24 hours shows only 20% success.
3. Are there differences in managing primary (baby) and permanent teeth dental trauma?
Yes, substantial differences determine appropriate management. Primary tooth trauma typically doesn’t warrant replantation due to infection risks and potential permanent tooth bud damage. However, permanent tooth trauma usually requires replantation if possible. Fractured primary teeth frequently heal with simple observation and conservative management, while fractured permanent teeth may require vital pulp therapy or endodontic treatment. Treatment protocols vary significantly based on tooth maturity and developmental stage—pediatric trauma management requires specialized expertise accounting for developing dentition.
4. What’s the difference between complete and incomplete jaw fractures and their treatment?
Complete fractures (full thickness across bone) require surgical stabilization through rigid fixation (plates and screws) or intermaxillary fixation (jaw wiring). These typically involve obvious displacement and functional limitations. Incomplete or greenstick fractures involve partial bone breaks maintaining structural continuity—these may heal conservatively with diet modification and mechanical protection. Classification requires imaging assessment—even seemingly minor fractures may be unstable. Conservative management risks malunion (improper healing) creating permanent bite problems. Specialized assessment ensures appropriate treatment approach.
5. How long does facial swelling typically last following maxillofacial trauma?
Initial facial swelling peaks approximately 24-72 hours post-injury, then gradually resolves over 2-4 weeks. Complete swelling resolution enabling final aesthetic assessment frequently requires 3-6 months. Residual swelling beyond this timeline may indicate infection, improper healing, or other complications requiring professional assessment. Ice application during the first 48 hours minimizes swelling progression. Anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDs) supports swelling reduction. Most swelling represents normal inflammatory response supporting healing rather than pathologic concern.
6. What treatment duration should patients expect for severe maxillofacial trauma?
Minor dental trauma may heal within 2-4 weeks, moderate injuries typically require 6-12 weeks healing, while severe complex trauma frequently requires months to years of staged reconstruction. Initial emergency treatment and acute healing phase typically requires 1-2 weeks, subacute rehabilitation phase 2-6 weeks, followed by long-term reconstruction phase potentially spanning months. Realistic expectation-setting enables patients to understand recovery progression and maintain motivation. DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic provides individualized recovery timelines based on specific injury characteristics.
7. How are surgical safety and sterilization protocols maintained during maxillofacial trauma care?
DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic implements hospital-grade sterilization protocols including: advanced autoclave sterilization of all surgical instruments, single-use sterile instrument packages for each patient, meticulous surgical field preparation preventing infection, strict aseptic technique throughout surgical procedures, appropriate personal protective equipment for surgical team, and antibiotic prophylaxis as indicated. These stringent protocols minimize infection risk—one of the most serious trauma care complications. Patients should inquire about facility accreditation and sterilization protocols when selecting trauma care providers.
8. What post-trauma reconstruction options exist for severely damaged facial structures?
Reconstruction approaches depend on injury severity and tissue loss extent. Minor soft tissue loss heals through primary closure. Moderate defects require local flap rotation or advancement restoring contour. Larger defects benefit from bone and cartilage grafting providing structural support. Extensive defects may require free tissue transfer (microsurgical reconstruction) restoring complex three-dimensional structure and function. Contemporary regenerative approaches including platelet-rich fibrin and stem cell therapies enhance healing potential. Advanced imaging and surgical planning enable sophisticated reconstruction restoring appearance and function even in severely damaged cases.
9. Are there specialized treatments for children following facial trauma different from adults?
Yes, pediatric trauma management emphasizes protection of developing dentition while managing acute injuries. Treatment approaches differ substantially between primary, mixed, and permanent dentition groups. Pediatric management prioritizes vital pulp preservation supporting continued root development. Conservative approaches prevent damage to underlying permanent tooth buds from traumatized primary teeth. Psychological support and anxiety management prove essential in pediatric trauma care. Child-friendly communication and gentle techniques reduce anxiety enabling optimal treatment. DrKhuntia’s Dental Clinic provides specialized pediatric trauma protocols addressing these unique requirements.
10. When can patients return to normal eating and speaking following maxillofacial trauma?
Return timeline depends on injury type and treatment approach. Initial liquid diet typically continues 1-2 weeks post-injury, progressing to soft foods over the following 2-4 weeks as pain resolves and healing advances. Progressive diet advancement follows professional guidance confirming adequate healing. Complete return to unrestricted diet typically occurs 6-12 weeks post-injury depending on complexity. Speech typically improves gradually as swelling resolves and oral tissues heal, though severe soft tissue injuries or jaw fractures may create temporary speech difficulties requiring speech therapy. Progressive functional advancement follows professional guidance—premature return to normal function risks complications.